


Given: 10.10.10.0/22 1- Create Network ID for the following LANs: LAN 1 = 12 Hosts LAN2 = 20 Hosts LAN3 = 225 Hosts LAN4 - 50 Hosts WAN 1 - 2 WAN2 - 2 2- Configure IP address to all devices on the VLSM-Topology in the files folder. Given: 10.10.10.0/22 1- Create Network ID for the following LANs: LAN 1 = 12 Hosts LAN2 = 20 Hosts LAN3 = 225 Hosts LAN4 - 50 Hosts WAN 1 - 2 WAN2 - 2 Physical 404 Physical Cat Services Programming Asus Conheur Conti B Server Ser OD San CHO A heged Server Server INA 250 PCO See More 21 000 Server 00D ATT WAND SW PPT PCE Pe Can Ow NEA ROPE FC ULA EFFEC PORT ACY Server OS Server RO FO 02 PF CS A Realtime Simulatie Auch Com A MacBook All 169.254.154.22).Transcribed image text: V Tools Donu 04 Sat 112 PM Cisco Pocket Tracer E Logical. (any device as Laptop)Andcheck the DHCP for IP addressAs shown, the DHCP failed and the APIPA (Automatic Private IP Address) is being usedTry to remove. DHCP failed : APIPA is being used my config interface FastEthernet0/1 description pc switchport access vlan 10 switchport mode access no shutdown interface FastEthernet0/2 description pc switchport access vlan 10 switchport mode access no shutdown interface Vlan1 description Management Vlan ip default-gateway 10.10.10.
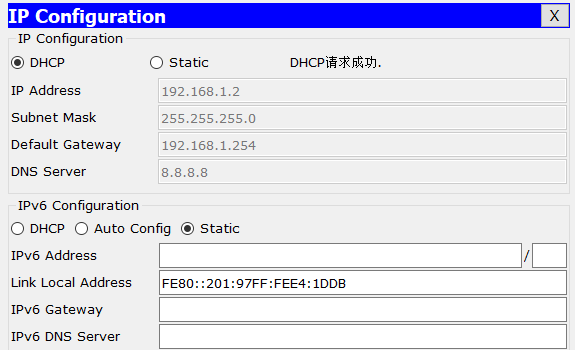
After some time (from a couple of seconds to a couple of minutes, depending on the operating system) the client auto-configures itself with an address from the APIPA range (e.g. However, the DHCP server is down and can’t respond to the host. The host boots up and looks for DHCP servers on the network. The host on the left is configured as DHCP client. Microsoft added Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA) to Windows XP to let machines on the same subnet communicate with one another when no DHCP server is.

This way, the host will still be able to communicate with other hosts on the local network segment that are also configured for APIPA. If the client can’t communicate with the DHCP server, it uses APIPA to configure itself with an IP address from the APIPA range. When a DHCP client boots up, it looks for a DHCP server in order to obtain network parameters. Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA) is a feature in operating systems (such as Windows) that enables computers to automatically self-configure an IP address and subnet mask when their DHCP server isn’t reachable.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
